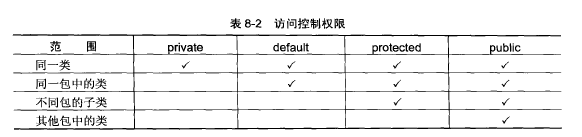
private default protected public的访问控制权限
protected范例
transient关键字 当使用Serializable接口实现序列化操作时,如果一个对象中的某一属性不希望被序列化,则可以使用transient关键字进行声明
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.Serializable; class Person_3 implements Serializable{ //此类的对象可以被序列化 private transient String name; private int age; public Person_3(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "姓名:" + name + ", 年龄:" + age; } } public class Serializable_demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 // File f = new File("/home/common/software/coding/HelloWord/HelloWord/test.txt");//路径 // ObjectOutputStream oos = null; // OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f); //文件输出流 // oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); //为对象输出流实例化 // oos.writeObject(new Person_3("张三", 30)); // oos.close(); File f = new File("/home/common/software/coding/HelloWord/HelloWord/test.txt");//路径 ObjectInputStream ois = null; InputStream input = new FileInputStream(f); //文件输入流 ois = new ObjectInputStream(input); //为对象输入流实例化 Object obj = ois.readObject(); //读取对象 ois.close(); System.out.println(obj); } }
<3>序列化一组对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.Serializable; class Person_3 implements Serializable{ //此类的对象可以被序列化 // private transient String name; private String name; private int age; public Person_3(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "姓名:" + name + ", 年龄:" + age; } } public class Serializable_demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 // File f = new File("/home/common/software/coding/HelloWord/HelloWord/test.txt");//路径 // ObjectOutputStream oos = null; // OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f); //文件输出流 // oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); //为对象输出流实例化 // oos.writeObject(new Person_3("张三", 30)); // oos.close(); // File f = new File("/home/common/software/coding/HelloWord/HelloWord/test.txt");//路径 // ObjectInputStream ois = null; // InputStream input = new FileInputStream(f); //文件输入流 // ois = new ObjectInputStream(input); //为对象输入流实例化 // Object obj = ois.readObject(); //读取对象 // ois.close(); // System.out.println(obj); Person_3 per[] = {new Person_3("张三",30),new Person_3("李四",31),new Person_3("王五",32)};//定义对象数组 ser(per); //序列化对象数组 Object o[] = dser(); for(int i=0;i<o.length;i++){ Person_3 p = (Person_3) o[i]; System.out.println(p); } } public static void ser(Object obj[]) throws Exception{ File f = new File("/home/common/software/coding/HelloWord/HelloWord/test.txt");//路径 ObjectOutputStream oos = null; OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f); //文件输出流 oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); //为对象输出流实例化 oos.writeObject(obj); oos.close(); } public static Object[] dser() throws Exception{ File f = new File("/home/common/software/coding/HelloWord/HelloWord/test.txt");//路径 ObjectInputStream ois = null; InputStream input = new FileInputStream(f); //文件输入流 ois = new ObjectInputStream(input); //为对象输入流实例化 Object obj[] = (Object[])ois.readObject(); //读取对象数组 ois.close(); return obj; } }
volatile关键字 一旦一个共享变量(类的成员变量、类的静态成员变量)被volatile修饰之后,那么就具备了两层语义:
保证了不同线程对这个变量进行操作时的可见性,即一个线程修改了某个变量的值,这新值对其他线程来说是立即可见的。
禁止进行指令重排序。
参考:Java并发编程:volatile关键字解析
final关键字 final在Java中表示的意思是最终,使用final关键字声明类属性、方法,注意:
1、使用final声明的类不能有子类
2、使用final声明的方法不能被子类所覆写
3、使用final声明的变量即成为常量、常量不可以修改
注意:final变量的命名规则
在使用final声明变量的时候,要求全部的字母大写
如果一个程序中的变量使用public static final声明,则此变量将称为全局常量
super关键字 使用super关键字可以从子类中调用父类中的构造方法、普通方法和属性
与this调用构造方法的要求一样,语句必须放在子类构造方法的首行
this和super都可以调用构造方法,但是两者不能同时出现,调用构造的时候都必须放在构造方法的首行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 class person{ private String name; private int age; public person(String name,int age){ //构造方法 this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } // void print(){ //定义一个默认访问权限的方法 // System.out.println("Person---->void print()"); // } public String getInfo(){ return "姓名"+this.name+"年龄"+this.age; } } class student extends person{ private String school; //新定义的属性school public student(String name, int age,String school) { super(name, age); //指定调用父类中的构造方法 this.school = school; // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } public String getSchool() { return school; } public void setSchool(String school) { this.school = school; } // public void print(){ //覆写父类中的方法,扩大了权限 // super.print(); //调用父类中的print()方法 // System.out.println("student---->void print()"); // } public String getInfo(){ //覆写父类中的方法 return super.getInfo()+"学校"+this.school; //扩充父类中的方法 } } public class extends_demo { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 student person_1 = new student("李四",18,"清华大学"); // person_1.setName("张三"); // person_1.setAge(10); // person_1.setSchool("涵三中"); // System.out.println("姓名:"+person_1.getName()+"\n"+"年龄:"+person_1.getAge()+"\n"+"学校:"+person_1.getSchool()); // new student("张三",11,"三中").print(); System.out.println(person_1.getInfo()); //打印信息,调用覆写过的方法 person person_2 = new person("张三",18); System.out.println(person_2.getInfo()); } }
this和super的区别
区别
this
super
1.属性访问
访问本类中的属性,如果本类中没有此属性,则从父类中继续查找
访问父类中的属性
2.方法
访问本类中的方法,如果本类中没有此方法,则从父类中继续查找
直接访问父类中的方法
3.调用构造
调用本类构造,必须放在构造方法的首行
调用父类构造,必须放在子类构造方法的首行
4.特殊
表示当前对象
无此概念
static关键字 1.static申明属性 如果有属性希望被所有对象共享,则必须将其申明为static属性。
使用static声明属性,则此属性称为全局属性,有时候也称为静态属性。
当一个类的属性申明为static的时候,由这个类产生的多个对象中属性,只需要对其中一个对象的该属性进行修改 ,即可以修改所有对象的这个属性 。
若只申明为public,没有static的时候,则修改申明的对象的属性只修改一个,申明为private的时候报错,因为该属性私有化,不能被方法所调用。
在调用static申明的属性的时候,最好通过类名称来直接调用,因为通过对象来调用不知道该类产生了多少的对象,这样子不太好,所以又把static声明的属性称为类属性,调用的格式位Person_1.coountry=”B city”;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Person_1{ private String name; private int age; static String country = "A city"; public Person_1(String n,int a){ this.name = n; this.age = a; } public void info(){ System.out.println("name:"+this.name+"\t"+"age:"+this.age+"\t"+"city:"+this.country); } }; public class static_test { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Person_1 p1 = new Person_1("zhangsan",30); Person_1 p2 = new Person_1("wangwu",40); p1.info(); p2.info(); p1.country = "B city"; p1.info(); p2.info(); } }
输出
1 2 3 4 5 name:zhangsan age:30 city:A city name:wangwu age:40 city:A city name:zhangsan age:30 city:B city name:wangwu age:40 city:B city
2.static申明方法 使用static申明的方法又称为类方法,Person_1.setCountry(“B city”); 同时修改多个对象的属性
非static声明的方法可以去调用static声明的属性或方法
但是static声明的方法是不能调用非static类型声明的属性或者方法的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Person_1{ private String name; private int age; public static String country = "A city"; public static void setCountry(String c){ country = c; } public static String getCountry(){ return country; } public Person_1(String n,int a){ this.name = n; this.age = a; } public void info(){ System.out.println("name:"+this.name+"\t"+"age:"+this.age+"\t"+"city:"+this.country); } }; public class static_test { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Person_1 p1 = new Person_1("zhangsan",30); Person_1 p2 = new Person_1("wangwu",40); p1.info(); p2.info(); //p1.country = "B city"; Person_1.setCountry("B city"); p1.info(); p2.info(); } }
可以通过static还统计实例化了多少个对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class demo{ private static int count = 0; public demo(){ count++; System.out.println("No."+count); } } public class static_count { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 new demo(); new demo(); new demo(); } }
给主方法的args传递参数,然后统计传递的参数的个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class HelloWprdApp { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int num = 0,sum = 0; char num1 = 97; if(args.length != 3){ System.out.println("<3"); System.exit(1); } for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){ System.out.println("name:"+args[i]); } } }
Java其他关键字 public:表示此方法可以被外部调用
static:表示此方法可以由类名称直接调用
void:主方法是程序的起点,所以不需要任何的返回值
main:系统规定好默认调用的方法名称,执行时默认找到main方法名称
String arg[]:表示的是运行 时的参数。参数传递的形式为“Java类名称 参数1 参数2…”