CyclicBarrier
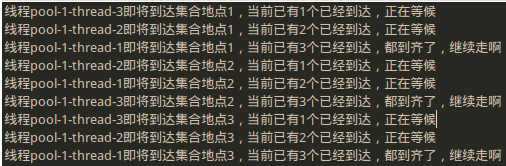
适用于:创建一组任务,它们并行地执行任务,然后在进行下一个步骤之前等待 ,直至所有任务完成。它使得所有的并行任务都将在栅栏处列队,因此可以一致地向前移动。
表示大家彼此等待,大家集合好后才开始出发,分散活动后又在指定地点集合碰面,这就好比整个公司的人员利用周末时间集体郊游一样,先各自从家出发到公司集合后,再同时出发到公园游玩,在指定地点集合后再同时开始就餐…
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package java_thread; import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class CyclicBarrierTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); final CyclicBarrier cb = new CyclicBarrier(3); for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){ public void run(){ try { Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*10000)); System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "即将到达集合地点1,当前已有" + (cb.getNumberWaiting()+1) + "个已经到达," + (cb.getNumberWaiting()==2?"都到齐了,继续走啊":"正在等候")); cb.await(); Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*10000)); System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "即将到达集合地点2,当前已有" + (cb.getNumberWaiting()+1) + "个已经到达," + (cb.getNumberWaiting()==2?"都到齐了,继续走啊":"正在等候")); cb.await(); Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*10000)); System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "即将到达集合地点3,当前已有" + (cb.getNumberWaiting() + 1) + "个已经到达," + (cb.getNumberWaiting()==2?"都到齐了,继续走啊":"正在等候")); cb.await(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; service.execute(runnable); } service.shutdown(); } }
倒计时器CountDownLatch
犹如倒计时计数器,调用CountDownLatch对象的countDown方法就将计数器减1,当计数到达0时,则所有等待者或单个等待者开始执行 。这直接通过代码来说明CountDownLatch的作用,这样学员的理解效果更直接。 可以实现一个人(也可以是多个人)等待其他所有人都来通知他,这犹如一个计划需要多个领导都签字后才能继续向下实施。还可以实现一个人通知多个人的效果,类似裁判一声口令,运动员同时开始奔跑。用这个功能做百米赛跑的游戏程序不错哦!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package java_thread; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class CountdownLatchTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); final CountDownLatch cdOrder = new CountDownLatch(1); final CountDownLatch cdAnswer = new CountDownLatch(3); for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){ public void run(){ try { System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正准备接受命令"); cdOrder.await(); //等待计数器归零 System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已接受命令"); Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*10000)); System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "回应命令处理结果"); cdAnswer.countDown(); //减小主线程计数值 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; service.execute(runnable); } try { //主线程 Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*10000)); System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "即将发布命令"); cdOrder.countDown(); //减小计数值 System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已发送命令,正在等待结果"); cdAnswer.await(); //等待计数器归零 System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已收到所有响应结果"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } service.shutdown(); } }
Exchanger
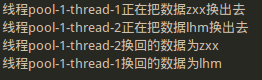
用于实现两个人之间的数据交换,每个人在完成一定的事务后想与对方交换数据,第一个先拿出数据的人将一直等待第二个人拿着数据到来时,才能彼此交换数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package java_thread; import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class ExchangerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); final Exchanger exchanger = new Exchanger(); service.execute(new Runnable(){ public void run() { try { String data1 = "zxx"; System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在把数据" + data1 +"换出去"); Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*10000)); String data2 = (String)exchanger.exchange(data1); System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "换回的数据为" + data2); }catch(Exception e){ } } }); service.execute(new Runnable(){ public void run() { try { String data1 = "lhm"; System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在把数据" + data1 +"换出去"); Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*10000)); String data2 = (String)exchanger.exchange(data1); System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "换回的数据为" + data2); }catch(Exception e){ } } }); } }