多个线程要操作同一资源 时就有可能出现资源的同步问题 。
同步 就是指多个操作在同一个时间段内只能有一个线程进行,其他线程要等待此线程完成之后才可以继续执行。
解决资源共享的同步操作,可以使用同步代码块 和同步方法 两种方式完成。
<1>同步代码块
所谓代码块就是指使用“{}”括起来的一段代码,根据其位置和声明的不同,可以分为普通代码块、构造块、静态块3种,如果在代码块上加上synchronized关键字 ,则此代码块就称为同步代码块。
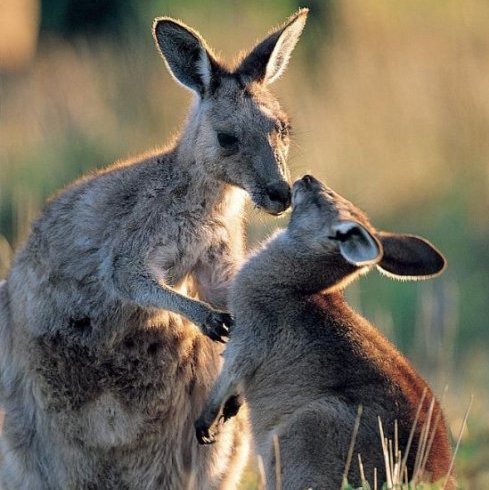
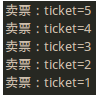
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 package java_thread; class MyThread_2 implements Runnable{ private int ticket = 5; @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 for (int i=0;i<10;i++){ synchronized (this) { //设置需要同步的操作 if(ticket>0){ try{ Thread.sleep(300); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("卖票:ticket="+ticket--); } } // this.sale(); //调用同步方法 } } } public class Runnable_demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 MyThread_2 mt = new MyThread_2(); //实例化Runnable子类对象 Thread t1 = new Thread(mt); //实例化Thread类对象 Thread t2 = new Thread(mt); //实例化Thread类对象 Thread t3 = new Thread(mt); //实例化Thread类对象 t1.start(); //启动线程 t2.start(); //启动线程 t3.start(); //启动线程 } }
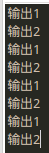
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 package java_thread; class Output{ public void output(String name){ int len = name.length(); synchronized(this){ //不能使用name,因为“输出1”和"输出2"两个字符串不是同一个对象 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ System.out.print(name.charAt(i)); } System.out.println(); } } } public class Huchi { private void init(){ final Output outputer = new Output(); //线程1 new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 while(true){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } //new Output().output("输出1"); //也不能new对象,new对象的话,this就不代表同一个对象了 outputer.output("输出1"); } } }).start(); //线程2 new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 while(true){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } //new Output().output("输出1"); //也不能new对象,new对象的话,this就不代表同一个对象了 outputer.output("输出2"); } } }).start(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 new Huchi().init(); } }
<2>同步方法
也可以使用synchronized关键字 将一个方法声明成同步方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class MyThread_2 implements Runnable{ private int ticket = 5; @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 for (int i=0;i<10;i++){ this.sale(); //调用同步方法 } } public synchronized void sale(){ //声明同步方法 if(ticket>0){ try{ Thread.sleep(300); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("卖票:ticket="+ticket--); } } } public class Runnable_demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 MyThread_2 mt = new MyThread_2(); //实例化Runnable子类对象 Thread t1 = new Thread(mt); //实例化Thread类对象 Thread t2 = new Thread(mt); //实例化Thread类对象 Thread t3 = new Thread(mt); //实例化Thread类对象 t1.start(); //启动线程 t2.start(); //启动线程 t3.start(); //启动线程 } }
死锁 就是指两个线程都在等待彼此先完成,造成了程序的停滞,一般程序的死锁都是在程序运行时出现的。
多个线程共享同一资源时需要进行同步,以保证资源操作的完整性,但是过多的同步就有可能产生死锁。
生产者不断生产,消费者不断取走生产者生产的产品
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 class Info{ private String name = "张三"; private String content = "学生"; private boolean flag = false; public synchronized void set(String name,String content){ //设置信息名称及内容 if(!flag){ //标志位为false,不可以生产,在这里等待取走 try{ super.wait(); //等待消费者取走 }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } this.setName(name); //设置信息名称 try{ Thread.sleep(300); //加入延迟 }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } this.setContent(content); //设置信息内容 flag = false; //标志位为true,表示可以取走 super.notify(); //唤醒等待线程 } public synchronized void get(){ //取得信息内容 if(flag){ //标志位为true,不可以取走 try{ super.wait(); //等待生产者生产 }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } try { Thread.sleep(300); //加入延迟 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(this.getName()+"-->"+this.getContent()); //输出信息 flag = true; //修改标志位为true,表示可以生产 super.notify(); //唤醒等待线程 } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } } class Producer implements Runnable{ //定义生产者线程 private Info info = null; //保存Info引用 public Producer(Info info) { //构造函数 super(); this.info = info; } @Override public void run() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 boolean flag = false; for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ //50次反复修改name和content的值 if(flag){ this.info.set("张三", "学生"); flag = false; }else{ this.info.set("李四", "老师"); flag = true; } } } } class Consumer implements Runnable{ //定义生产者线程 private Info info = null; //保存Info引用 public Consumer(Info info) { //构造函数 super(); this.info = info; } @Override public void run() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ //50次反复修改name和content的值 try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.info.get(); } } } public class ThreadInfo_demo { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Info i = new Info(); Producer pro = new Producer(i); Consumer con = new Consumer(i); new Thread(pro).start(); new Thread(con).start(); } }
停止线程运行
在多线程的开发中可以通过设置标志位的方式停止一个线程的运行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class MYThread implements Runnable{ private boolean flag = true; //定义标志位属性 @Override public void run() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 int i = 0; while(this.flag){ //循环输出 while(true){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+(i++)); //输出当前线程名称 } } } public void stop(){ //编写停止方法 this.flag = false; //修改标志位 } } public class ThreadStop_demo { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 MYThread my = new MYThread(); Thread t = new Thread(my,"线程"); t.start(); my.stop(); } }
互斥性
output1和output2两段代码互斥,检查的都是outputer这个对象
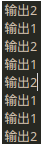
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 package java_thread; class Output{ public void output(String name){ int len = name.length(); synchronized(this){ //不能使用name,因为“输出1”和"输出2"两个字符串不是同一个对象 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ System.out.print(name.charAt(i)); } System.out.println(); } } public synchronized void output2(String name){ //output1和output2两段代码互斥,检查的都是outputer这个对象 int len = name.length(); for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ System.out.print(name.charAt(i)); } System.out.println(); } } public class Huchi { private void init(){ final Output outputer = new Output(); //线程1 new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 while(true){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } //new Output().output("输出1"); //也不能new对象,new对象的话,this就不代表同一个对象了 outputer.output("输出1"); } } }).start(); //线程2 new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 while(true){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } //new Output().output("输出1"); //也不能new对象,new对象的话,this就不代表同一个对象了 outputer.output2("输出2"); } } }).start(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 new Huchi().init(); } }
static静态方法调用的对象是字节码对象,所以要把output1的this改成Output.class
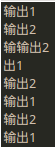
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package java_thread; class Output{ public void output1(String name){ int len = name.length(); synchronized(this){ //不能使用name,因为“输出1”和"输出2"两个字符串不是同一个对象 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ System.out.print(name.charAt(i)); } System.out.println(); } } //static静态方法调用的对象是字节码对象,所以要把output1的this改成Output.class public static synchronized void output3(String name){ //output1和output3不同步,除非把output1的this改成Output.class int len = name.length(); for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ System.out.print(name.charAt(i)); } System.out.println(); } } public class Huchi { private void init(){ final Output outputer = new Output(); //线程1 new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 while(true){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } //new Output().output("输出1"); //也不能new对象,new对象的话,this就不代表同一个对象了 outputer.output1("输出1"); } } }).start(); //线程2 new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { //覆写Thread类中的run()方法 while(true){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } //new Output().output("输出1"); //也不能new对象,new对象的话,this就不代表同一个对象了 outputer.output3("输出2"); } } }).start(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 new Huchi().init(); } }
this Output.class
面试题:子线程循环 10 次,接着主线程循环 100,接着又回到子线程循环 10 次,接着再回到主线程又循环 100,如此循环50 次,请写出程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 package java_thread; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; //张孝祥java面试题28 //子线程循环 10 次,接着主线程循环 100,接着又回到子线程循环 10 次,接着再回到主线程又循环 100,如此循环50 次,请写出程序 public class TraditionalThreadCommunication { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { final Business business = new Business(); new Thread( new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for(int i=1;i<=50;i++){ business.sub(i); } } } ).start(); for(int i=1;i<=50;i++){ business.main(i); } } } class Business { private boolean bShouldSub = true; public synchronized void sub(int i){ while(!bShouldSub){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } for(int j=1;j<=10;j++){ System.out.println("sub thread sequence of " + j + ",loop of " + i); } bShouldSub = false; this.notify(); } public synchronized void main(int i){ while(bShouldSub){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } for(int j=1;j<=100;j++){ System.out.println("main thread sequence of " + j + ",loop of " + i); } bShouldSub = true; this.notify(); } }